Add low fidelity engineering modeling¶
In this section, a few simplified engineering models are added to the example4
Evaulation¶
Command line
evaluate.py --input=evaluate.json --output=evaluate.dat --nsample=100000 --quiet
evaluate.json
{
"scan": {
"d_blanket" : {"type": "range", "ymin":0.2, "ymax":0.4},
"d_tf" : {"type": "range", "ymin":0.4, "ymax":1.2},
"d_cs" : {"type": "range", "ymin":0.2, "ymax":0.6},
"f_wp" : {"type": "range", "ymin":0.5, "ymax":0.8},
"f_r_tf_out": {"type": "range", "ymin":2.5, "ymax":4.5}
},
"const": {
"aratio" : 3.0,
"a" : 1.3333,
"kappa" : 2.0,
"delta" : 0.6,
"bt" : 7.0,
"ip" : 8.1,
"pinj" : 38.0,
"fgw_ped" : 1.0,
"nepeak" : 1.9,
"h98" : 1.4,
"eta_cd" : 0.25,
"eta_th" : 0.33,
"d_sol" : 0.1,
"d_str" : 0.1,
"gap_vv" : 0.05,
"d_vv" : 0.15,
"gap_shield" : 0.05,
"d_shield" : 0.225,
"gap_tf" : 0.083,
"gap_cs" : 0.08,
"t_helium" : 4.5,
"strain_sc" : -0.005,
"f_sc_copper" : 0.69,
"f_sc_helium" : 0.46,
"f_sc_conductor": 0.28
},
"model": {
"r" : ["expr", "a * aratio" ],
"betan_ped" : ["base", {} ],
"te_ped" : ["base", {"dependency":"betan_ped"} ],
"ti_ped" : ["expr", "te_ped" ],
"ngw" : ["base", {} ],
"ne_ped" : ["expr", "fgw_ped * ngw" ],
"ne_axis" : ["expr", "nepeak * ne_ped" ],
"betan" : ["file", "fitout.json" ],
"pfus" : ["file", "fitout.json" ],
"fbs" : ["file", "fitout.json" ],
"pnet" : ["base", {}],
"d_wp" : ["expr", "f_wp * d_tf"],
"r_tf" : ["expr", "r - ( a + d_sol + d_blanket + d_str + gap_vv + gap_shield + d_shield + gap_tf + d_tf )"],
"r_cs" : ["expr", "r_tf - ( gap_cs + d_cs )"],
"r_tf_out" : ["expr", "r + f_r_tf_out * a"],
"bmax" : ["base", {}],
"itf" : ["base", {}],
"jtf" : ["base", {}],
"tf_stress_axial" : ["base", {}],
"tf_stress_hoop" : ["base", {}],
"tf_stress" : ["expr", "tf_stress_axial + tf_stress_hoop"],
"jsc_crit" : ["base", {}],
"jtf_crit" : ["expr", "jsc_crit * f_sc_copper * f_sc_helium * f_sc_conductor" ],
"f_jtf_crit": ["expr", "jtf / jtf_crit"]
}
}
For the illustration purpose, one of the simplified radial build models is employed, which is mainly defined by the inboard thicknesses for a set of the tokamak structures including blanket (d_blanket), structure ring (d_str), vacuum vessel (d_vv), thermal shield (d_shield), TF coil (d_tf), and central solenoid (d_cs), along with the gaps between the structures (gap_vv, gap_shield, gap_tf, gap_cs). See the parametric geometry representation of tokamak and the definition of TokDesinger variables
For the CAT-like reference case (aratio = 3, pinj = 38 MW, fgw_ped = 1, h98 = 1.4), this example evaluates:
- TF coil stress (
tf_stress) = sum of the hoop (tf_stress_hoop) and axial (tf_stress_axial) stresses - TF coil current density in the winding pack (
jtf) to produce the target magnetic field (bt= 7 T at the plasma geometry centerr= 4 m) - TF coil current density limit in the winding pack (
jtf_crit) imposed by the critical superconductor coil current density (jsc_crit).
for a range of the radial build dimensions, in particular to decide a feasible thickness range of TF coil (d_tf) and blanket (d_blanket).
Filtering¶
The constraints used in this example are:
tf_stress< 500 MPajtf<jtf_critr_cs> 0.2 m
, where r_cs is the inner radius of central solenoid.
Command line
filter.py --input=filter.json --dbfile=evaluate.dat --output=filter.dat
filter.json
{
"filter": {
"tf_stress" : ["max", 500.0],
"f_jtf_crit" : ["max", 1.0],
"r_cs" : ["min", 0.2]
}
}
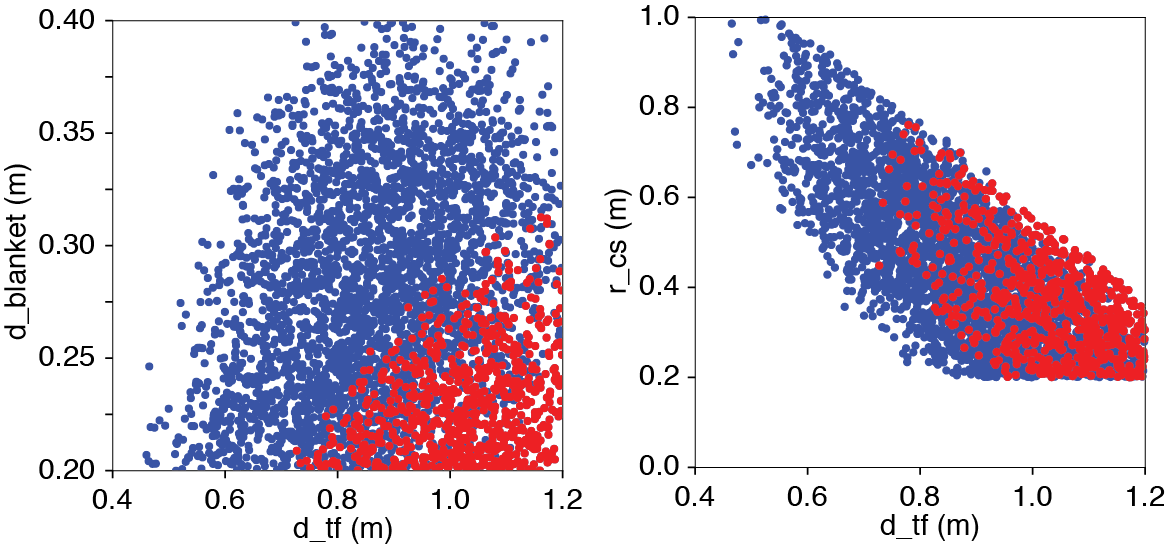
The blue + red points satisfy the radial build (r_cs > 0.2) and the TF coil stress constraint (tf_stress < 500 MPa). The red points satisfy additional superconductor current limit (jtf < jtf_crit).